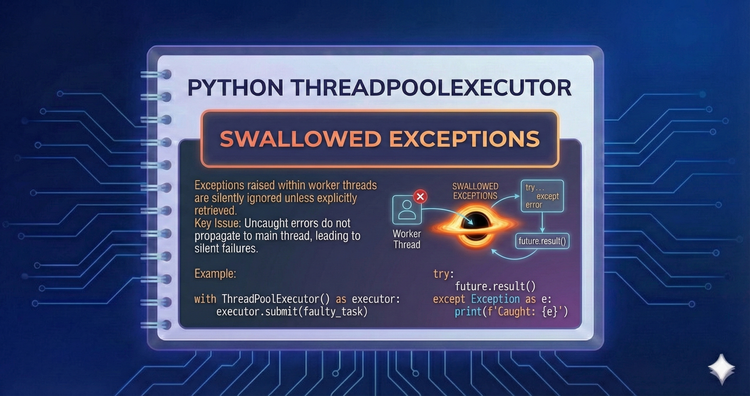
Python ThreadPoolExecutor - Swallowed Exceptions
A try/except block around .submit() only catches submission errors, not crashes inside the worker. We explain why errors occurring in background threads are isolated from the main program flow and how this silence can mask critical bugs.
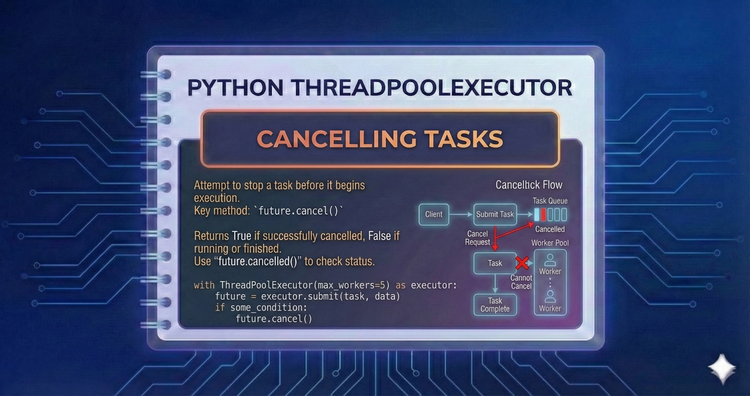
Python ThreadPoolExecutor - Cancelling Tasks
Not every task needs to finish. We discuss the limitations and mechanics of cancelling a Future, understanding when a task is too far gone to stop and how to handle CancelledError.
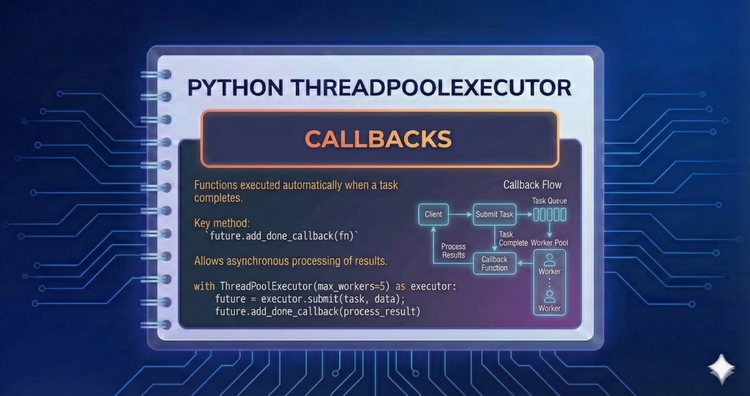
Python ThreadPoolExecutor - Callbacks
Keep the main thread free by attaching logic directly to the worker. We use add_done_callback to trigger post-processing functions automatically as soon as a background task completes.
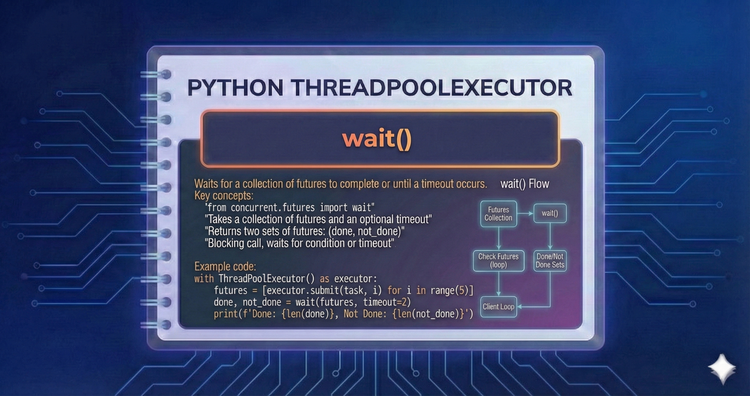
Python ThreadPool Executor - wait()
Sometimes you need to pause until specific milestones are reached. Learn to halt execution until the first task finishes, the first exception occurs, or all tasks are complete using the wait utility.
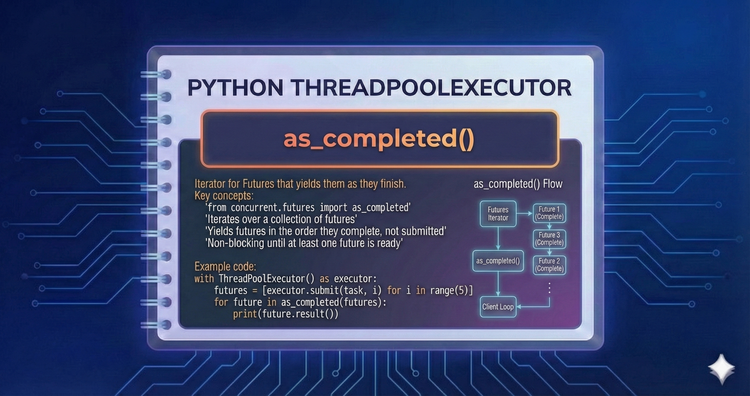
Python ThreadPool Executor - as_completed()
Often you need results as soon as they finish, regardless of submission order. We use as_completed to yield tasks the moment they finalize, creating highly responsive workflows.
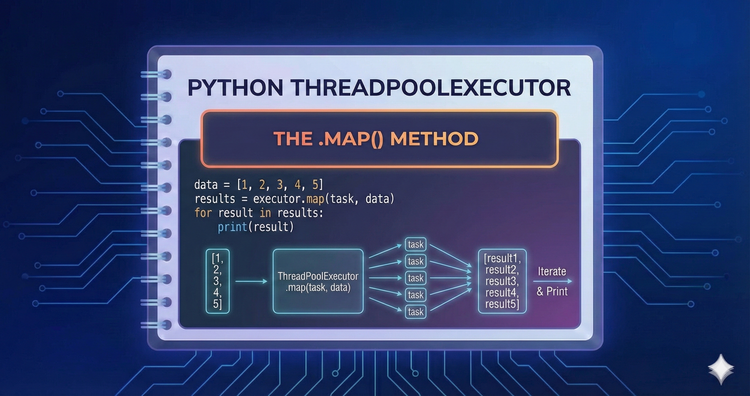
Python ThreadPoolExecutor - The .map() method
Parallelize an entire iterable with a single line of code. We compare this to the built-in map, showing how to process lists of data concurrently while preserving the order of results.
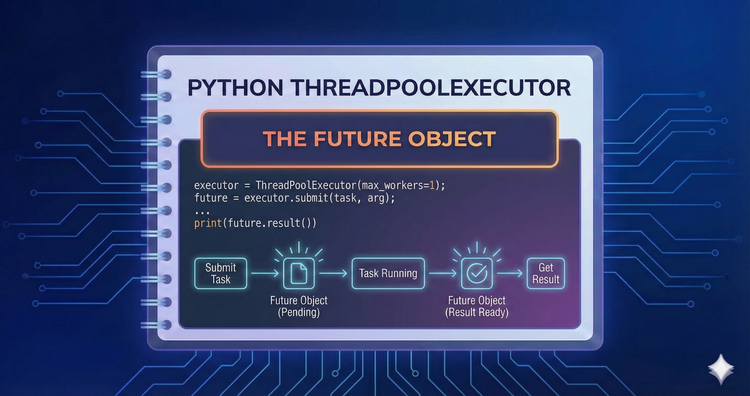
Python ThreadPoolExecutor - The Future Object
A Future represents a result that hasn't arrived yet. We explore how to query these objects to check if a task is running or done, and how to use the .result() method to retrieve the final value or error.
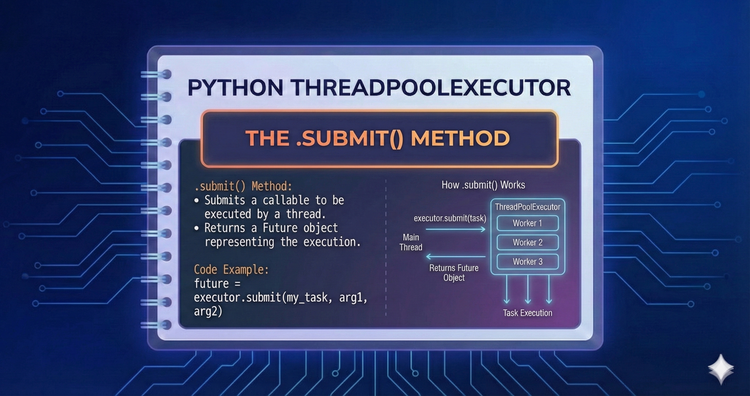
Python ThreadPoolExecutor - The .submit() Method
This is the core entry point for the Executor. Learn to schedule individual functions, pass arguments securely, and receive a Future object immediately, allowing the main program to continue without blocking.
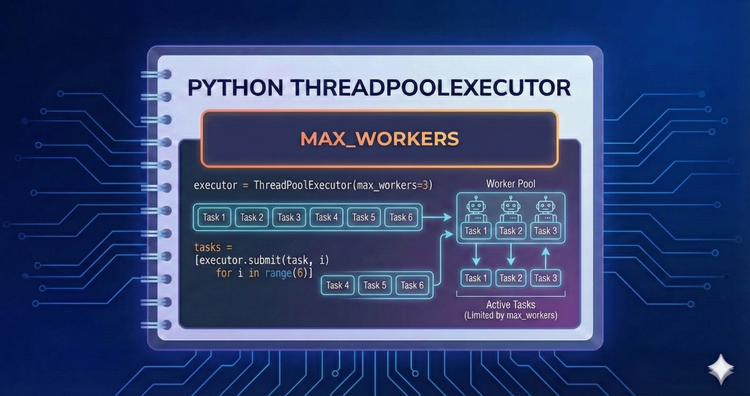
Python ThreadPoolExecutor - max_workers
Choosing the right number of threads is an art. We discuss how to tune the max_workers parameter based on your specific workload and how to avoid the performance penalty of context switching too many threads.
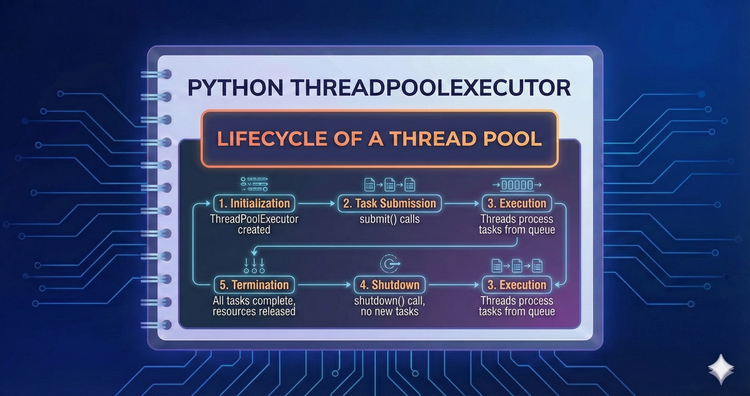
Python ThreadPoolExecutor - Lifecycle of a Thread Pool
A pool goes through distinct stages: initialization, task submission, and shutdown. We examine the internal state at each stage and how to manually control the lifecycle using .shutdown(wait=True) versus relying on the garbage collector.