Linear Algebra Series - Determinants
The determinant is a single number revealing a matrix's character. We use it to measure how transformations scale area or volume, and as a definitive test to check if a system is solvable or if a matrix can be inverted.
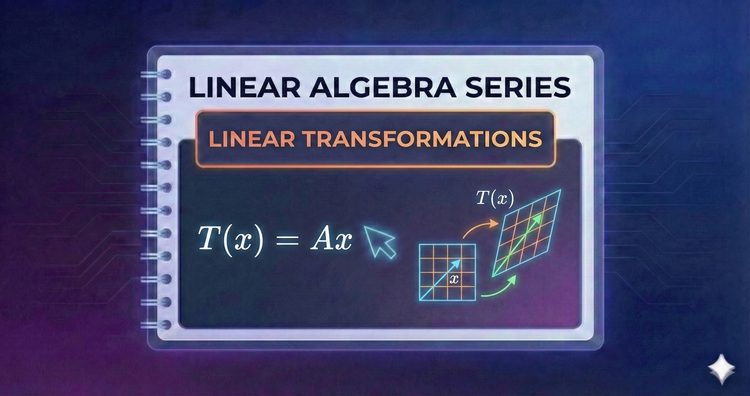
Linear Algebra Series - Linear Transformations
Viewing matrices as dynamic functions, we visualize them as "machines" that warp space. We see how they rotate, stretch, shear, and project vectors, forming the geometric core of computer graphics and animation.
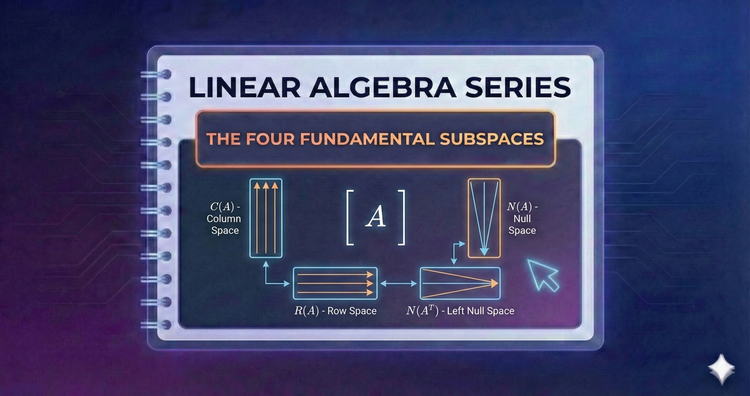
Linear Algebra Series - The Four Fundamental Subspaces
The "Big Picture" dissects a matrix into four components: Column, Row, Null, and Left Null spaces. We use the Rank-Nullity Theorem to reveal the intricate balance between the information a matrix preserves and what it destroys during transformation.
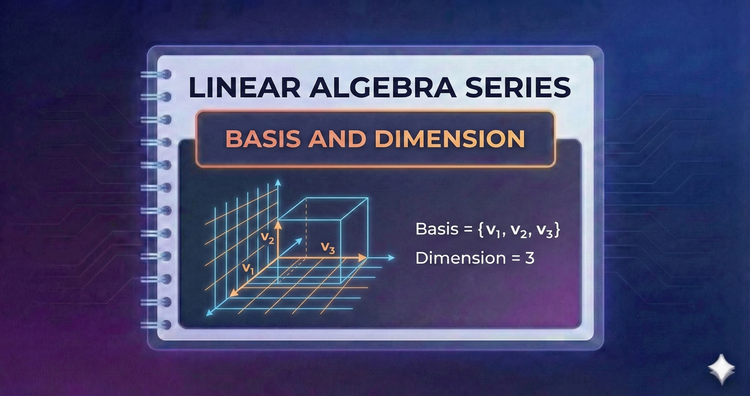
Linear Algebra Series - Basis and Dimension
To navigate space, you need a reference system. We define a "Basis"—the most efficient set of vectors to describe a space—and "Dimension," providing a precise mathematical method to measure the true size and complexity of any system.
Linear Algebra Series - General Vector Spaces
Moving from concrete arrows to abstract structure, we see that polynomials and functions obey the same laws as standard vectors. This abstraction allows us to apply powerful linear algebra tools to a vast array of complex mathematical problems.
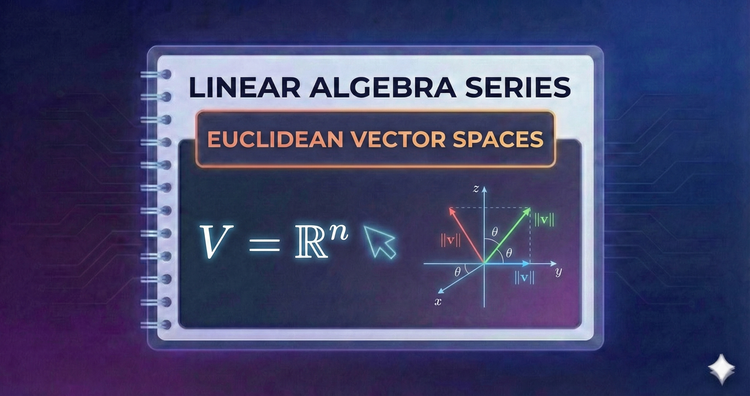
Linear Algebra Series - Euclidean Vector Spaces
We step into multidimensional space. By studying Linear Combinations and Span, we’ll learn how a few vectors can generate entire planes or volumes, establishing the fundamental rules for movement and navigation in 2D, 3D, and higher dimensions.
Linear Algebra Series - The Inverse Matrix
Division reverses multiplication for numbers; the Inverse Matrix does this for systems. We’ll learn to calculate the inverse to "undo" linear transformations and discover why "singular" matrices define systems that strictly cannot be reversed.
Linear Algebra Series - Matrix Algebra
Just as numbers have arithmetic, grids of numbers have their own algebra. We treat matrices as single units, mastering addition, scaling, and multiplication—operations that form the computational backbone of modern graphics processing and neural networks.
Linear Algebra Series - Systems of Linear Equations
Linear algebra starts with solving systems to find where lines and planes intersect. We’ll move beyond substitution to systematic algorithms like Gaussian Elimination, solving massive systems efficiently while determining if solutions exist and are unique.