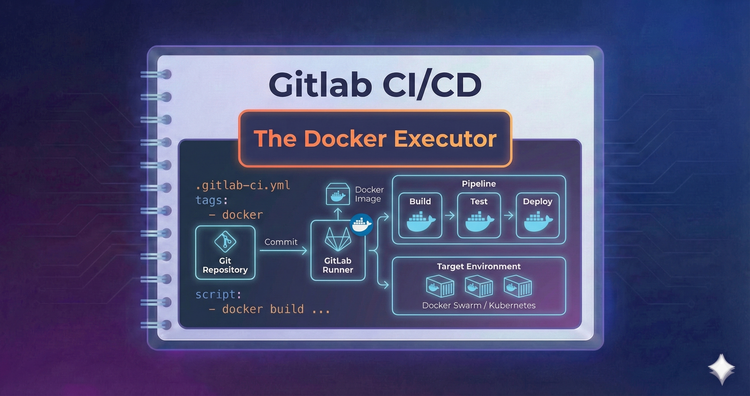
Gitlab CI/CD - The Docker Executor
Ideally, every job runs in a clean container. We’ll configure the Docker executor to pull specific images for each job, ensuring your tests run in the exact environment they need without polluting the host machine.
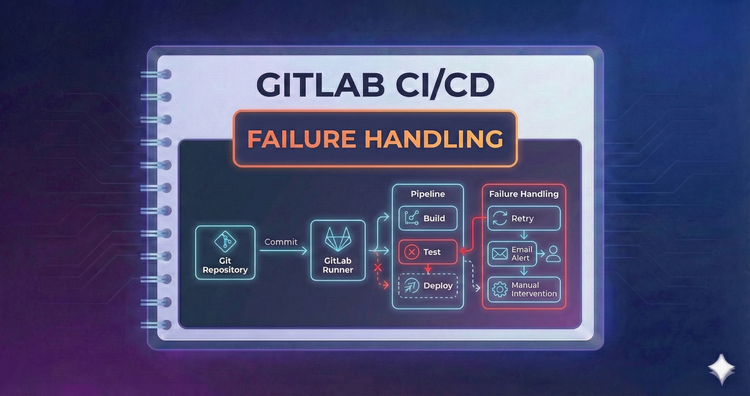
Gitlab CI/CD - Failure Handling
Flaky tests happen. We’ll configure allow_failure for non-critical jobs and use retry to automatically rerun jobs that fail due to temporary hiccups, ensuring your pipeline is robust against transient network issues.
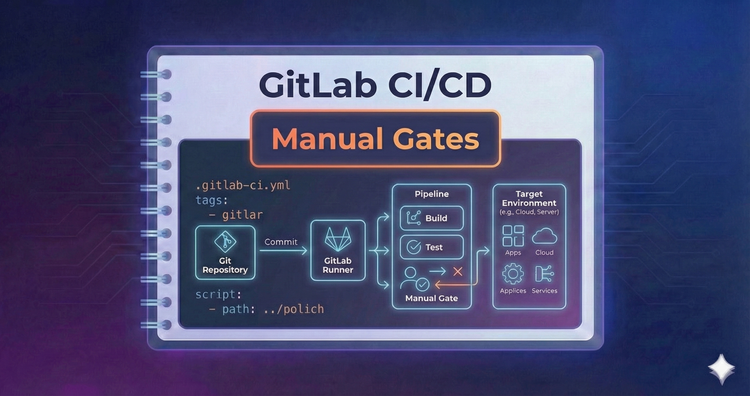
Gitlab CI/CD - Manual Gates
Not everything should deploy automatically. We’ll implement when: manual to create pause points in your pipeline, requiring authorized human intervention before proceeding to sensitive environments like Production.
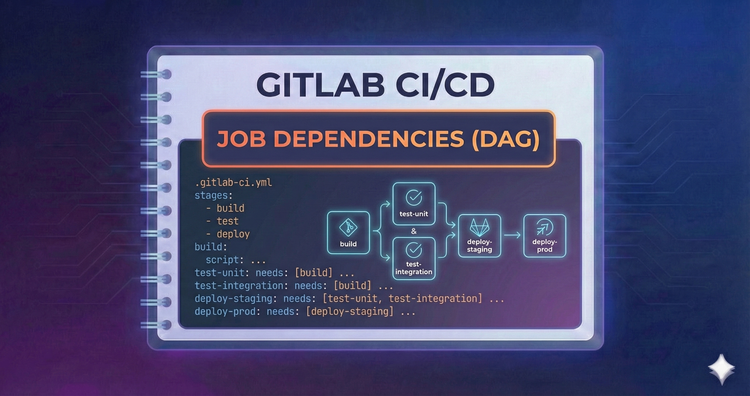
Gitlab CI/CD - Job Dependencies (DAG)
Sequential stages can be slow. With needs:, we break the stage order to create a Directed Acyclic Graph. This allows jobs to start immediately after their specific dependencies finish, drastically reducing wait times.
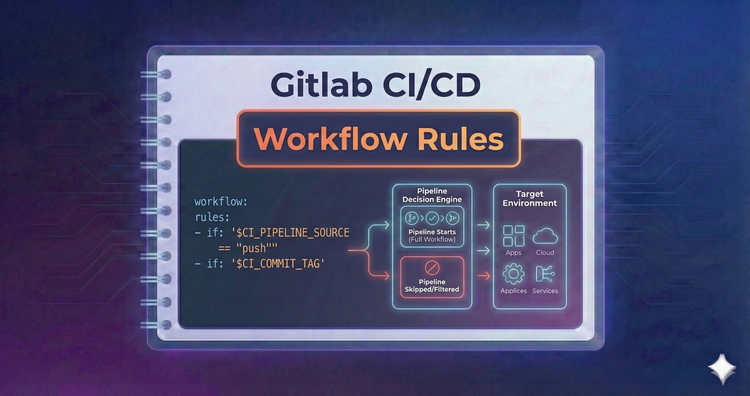
Gitlab CI/CD - Workflow Rules
Sometimes you need to control the entire pipeline, not just specific jobs. We’ll configure Workflow Rules to prevent duplicate pipelines from running on the same commit, such as stopping double runs on Merge Requests.
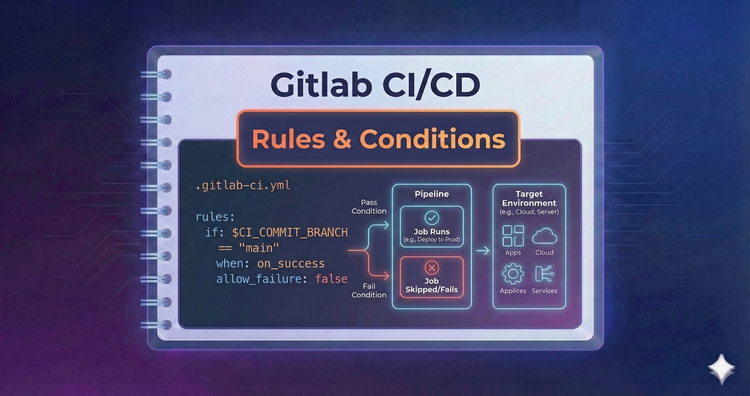
Gitlab CI/CD - Rules & Conditions
Modern pipelines need logic. We’ll replace legacy syntax with the powerful rules: keyword, allowing you to trigger jobs based on file changes, variable values, or the presence of specific files.
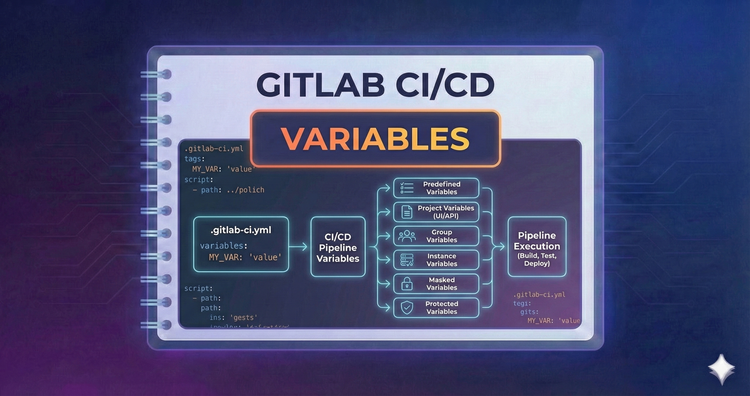
Gitlab CI/CD - Variables
Hardcoding values is a security risk. We’ll use CI/CD variables to manage configuration dynamically. Learn to use predefined variables for metadata and safe project settings for secrets like API keys and passwords.
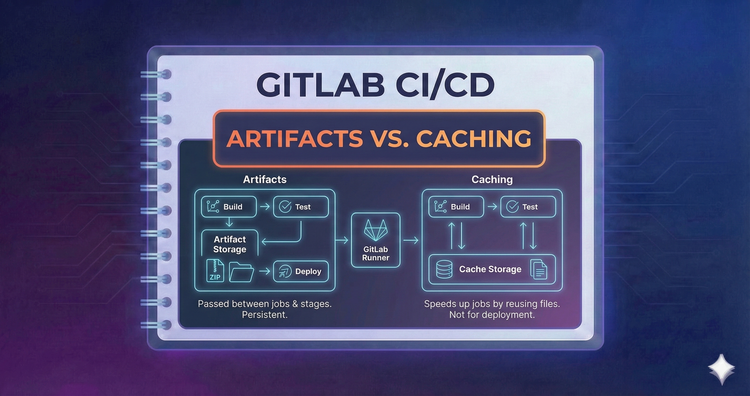
Gitlab CI/CD - Artifacts vs. Caching
Speed vs. Persistence. Use Caching to reuse dependencies like node_modules across pipelines to save time. Use Artifacts to pass build outputs, like binaries or test reports, between stages within a single pipeline run.
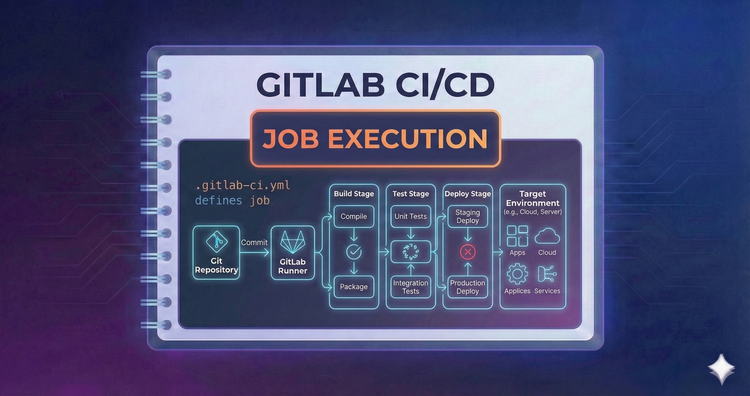
Gitlab CI/CD - Job Execution
Beyond the main script, lifecycle hooks like before_script and after_script handle setup and cleanup. Learn how to prepare your environment before a job runs and ensure vital cleanup steps happen even if the job fails.
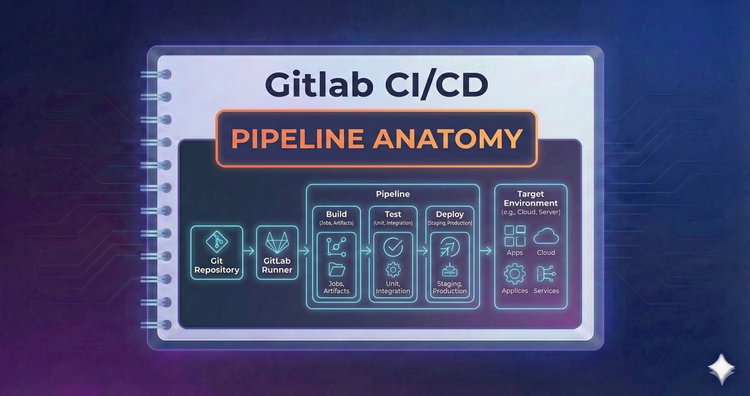
Gitlab CI/CD - Pipeline Anatomy
Pipelines are structured into Stages, Jobs, and Scripts. We'll dissect the YAML syntax to understand how stages define the execution order and how jobs encapsulate the actual commands that run your tests and builds.