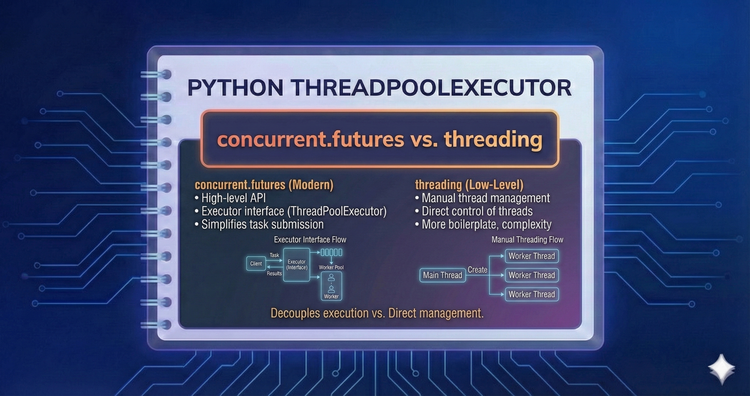
Python ThreadPoolExecutor - concurrent.futures vs. threading
Why use concurrent.futures over the old threading module? We demonstrate the manual boilerplate required by the legacy approach and how the Executor interface abstracts away the messy details.
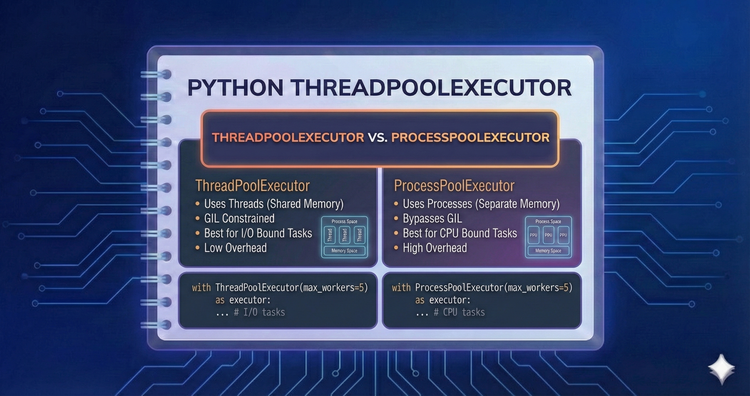
Python ThreadPoolExecutor - ThreadPoolExecutor vs. ProcessPoolExecutor
ThreadPoolExecutor isn't for everything. We contrast it with ProcessPoolExecutor, showing why CPU-heavy tasks need processes to bypass the GIL, while threads remain the superior choice for network and file I/O.
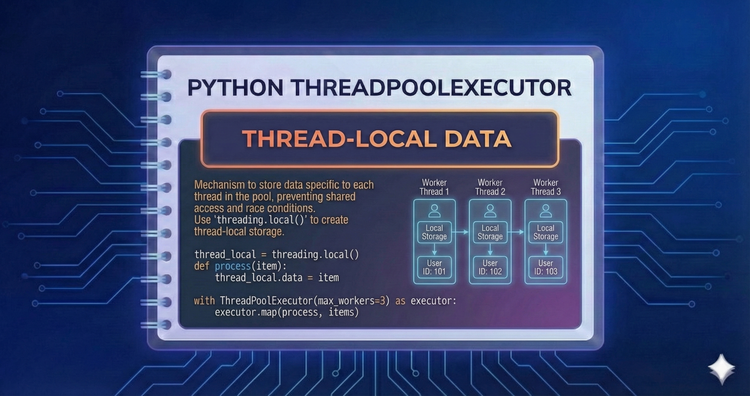
Python ThreadPoolExecutor - Thread-Local Data
Sometimes you need "global" variables that are unique to each thread. threading.local() creates thread-specific storage, allowing workers to maintain their own isolated state (like database connections) without interference.
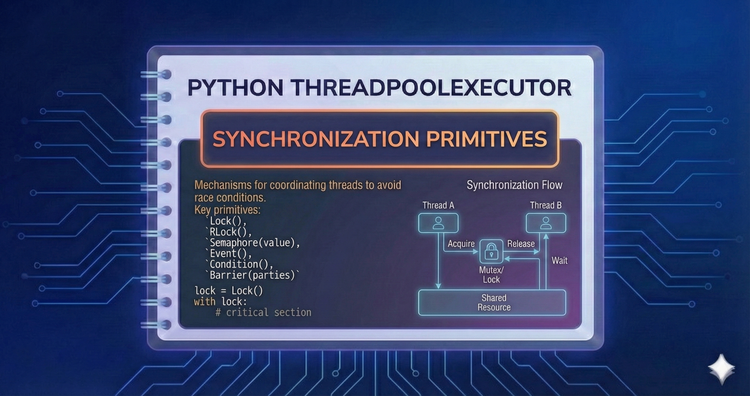
Python ThreadPoolExecutor - Synchronization Primitives
To protect critical sections, we use threading.Lock and RLock. These tools enforce mutual exclusion, acting like a traffic light that ensures only one thread can enter a protected block of code at a time.
Python ThreadPoolExecutor - Critical Sections
A critical section is a block of code that accesses a shared resource and must not be interrupted by other threads. We learn to identify these sensitive areas in your codebase where multiple threads overlapping would cause inconsistency.

Member discussion