Interactive Python Series - File I/O
Data persistence requires saving information to the disk so it survives after the program closes. We will cover how to read from and write to text files to create logs or save user progress.
Interactive Python Series - Exceptions
Errors are inevitable, but crashing your program doesn't have to be. Learn how to use try, except, and finally blocks to handle unexpected issues gracefully without stopping execution.
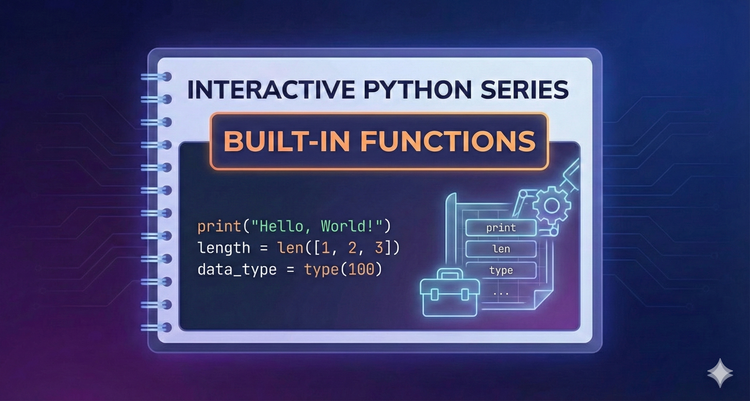
Interactive Python Series - Built-in Functions
Python comes batteries-included with powerful helpers that save you from writing standard logic from scratch. We’ll explore zip(), enumerate(), map(), and filter() to level up your coding efficiency.
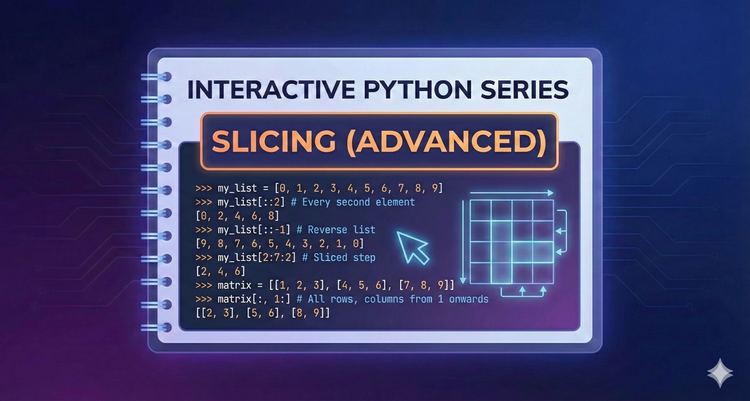
Interactive Python Series - Slicing (Advanced)
You know how to grab a piece of a list, but Python’s slicing syntax goes much deeper. Discover how to use strides to skip elements or reverse sequences instantly using [start:stop:step].
Interactive Python Series - String Formatting
Displaying data clearly is an art form, and Python offers several ways to inject variables into text. We will compare old formatting styles with modern f-Strings to show you the most readable and efficient approach.
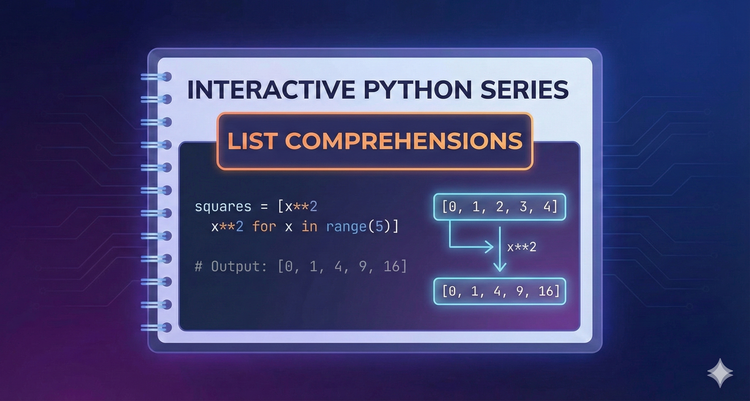
Interactive Python Series - List Comprehensions
Python is famous for its ability to condense a multi-line loop into a single, readable line of code. We’ll teach you list comprehension syntax to create new lists from existing iterables elegantly.
Interactive Python Series - Default Arguments
Making your functions flexible often means providing sensible default values for optional parameters. Learn how to implement default arguments to simplify function calls while retaining customization options.
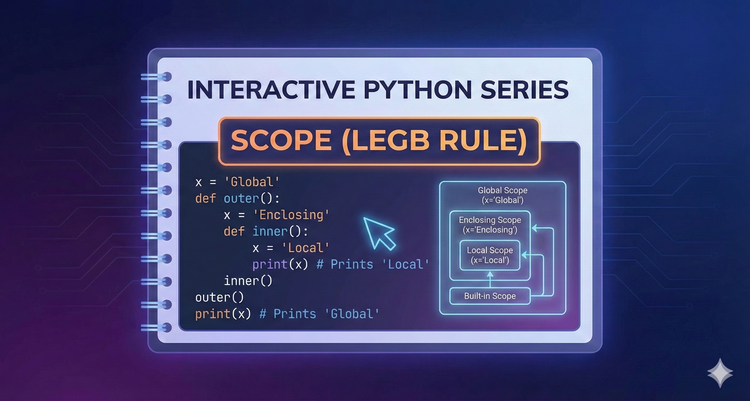
Interactive Python Series - Scope (LEGB Rule)
Variables aren't accessible everywhere, and understanding where they "live" prevents confusing errors. We will decode the LEGB rule (Local, Enclosing, Global, Built-in) to master variable visibility.
Interactive Python Series - Return Values
A function usually needs to send a result back to the main program after finishing its job. We will look at the return statement and how Python allows you to return multiple values easily using tuples.
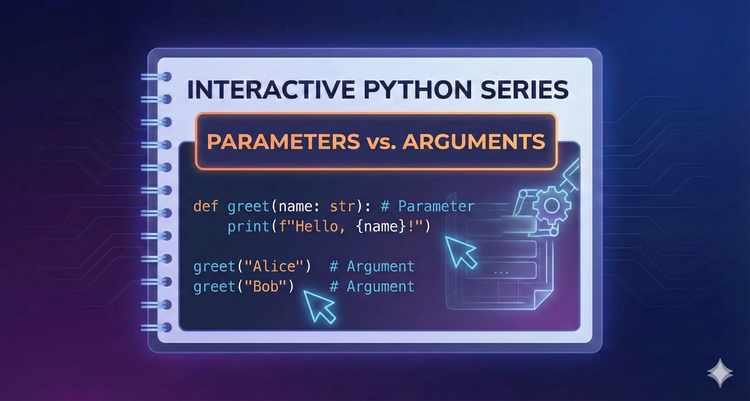
Interactive Python Series - Parameters vs. Arguments
Passing data into functions makes them dynamic and flexible for different situations. We’ll explain the distinction between parameters and arguments, including how to use keyword arguments for clarity.